Blood Cancer Surgery in India
Blood Cancer Surgery
Blood Cancer or Leukemia refers to a group of cancers of the blood cells. In blood cancer, white blood cells become abnormal, and divide and grow in an uncontrolled way. | 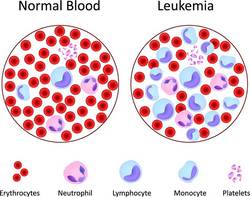 |
White blood cells and blood cancer
White blood cells are made in your bone marrow, which is the soft spongy centre of your bones. Your bone marrow makes the most basic type of cells (called stem cells), and they can develop further into three types of cells -
- white blood cells - protect your body from infection
- red blood cells - carry oxygen around your body
- platelets - important for normal blood clotting
Once these cells are made, they enter your bloodstream. White blood cells are involved in your body's immune system, a defense system that protects you from infections. There are two main types of white blood cells - myeloid cells and lymphocytes.
In blood cancer, some of the white blood cells don't grow properly. They stay in the bone marrow and keep reproducing in an uncontrolled way. These abnormal white blood cells fill up the bone marrow and prevent it from making healthy white blood cells. This means the body is less able to fight off infections. The abnormal white blood cells also prevent bone marrow from making enough red blood cells and platelets. A lack of red blood cells leads to less oxygen being delivered to the organs and tissues of your body. This is called anemia, and it can make you feel tired and breathless. A lack of platelets can lead to problems with the blood-clotting system, and results in bleeding and bruising much more easily than usual.
Causes of Blood Cancer
The exact cause of blood cancer is unknown, although there are some factors that increase the chance of developing it.
These include :
- A weakened immune system - this may be a result of medicines that suppress the immune system (eg medicines to prevent rejection of organ transplants), high doses of radiation (eg radiotherapy or chemotherapy for another cancer), or diseases that affect the immune system (eg HIV)
- Age - chronic leukemia is more common in people who are over 40
- Gender - slightly more men than women are affected by leukemia
- Smoking
- Certain genetic conditions, such as Down's syndrome
- Other blood disorders, such as aplastic anemia, a rare condition where the bone marrow fails to produce blood cells correctly
- Contact with a chemical called benzene, one of the chemicals in petrol and a solvent used in the rubber and plastics industry
Types of Blood Cancer / Leukemia
There are several types of blood cancer. They are named according to the type of white blood cells (myeloid cells or lymphocytes) that are affected and how quickly the disease develops. Only the common types are discussed here. The two main types of blood cancer are acute and chronic.
Acute blood cancer
In acute blood cancer, symptoms develop rapidly and the cancer can quickly become life-threatening if it's not treated. The most common form of acute blood cancer affects lymphocytes. This is called acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). Another type of acute blood cancer is acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Chronic blood cancer
In chronic blood cancer, symptoms develop slowly and the white blood cells are almost fully grown and normal when they leave the bone marrow and enter the bloodstream. They can function, but not as well as they should do. One type of blood cancer, called chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), affects a particular type of white blood cells called myeloid cells. It has two phases, a chronic phase that can last for several years, during which symptoms develop slowly, followed by a more aggressive phase (accelerated phase), where symptoms quickly get worse.
Symptoms
The symptoms of blood cancer vary, depending on the exact type of disease and how advanced it is. There may be no symptoms in the early stages, especially in people with chronic blood cancer. Many symptoms are vague, such as fever, headaches, weight loss and night sweats.
Symptoms of blood cancer include –
- Tiredness, breathlessness and pale skin (due to anemia, a reduction in number of red cells in the blood)
- Frequent infections that do not get better
- Increased bruising
- Abnormal bleeding from gums and cuts
- Heavier periods in women
- Nosebleeds
- Bone pain (due to the pressure of a build-up of cells in the bone marrow)
- Swollen lymph glands (glands in the neck, groin and under the arms)
- Abdominal pain (due to an enlarged spleen or liver)
- Swollen gums, and occasionally, swollen testicles
- Headaches and vision problems
Treatment for Blood Cancer
The effectiveness of treatment for blood cancer depends on the type and stage of the disease. Acute blood cancer or acute leukemia often goes into remission (the symptoms go away; the disease is under control but not necessarily cured). But many people with acute blood cancer have a relapse (the disease returns).
Treatment includes
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Bone marrow or stem cell transplant
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Biological therapy (which may be in the form of tablets)
- Steroids
click here
Phone Numbers Reach Us-
India & International : +91-9860755000 / +91-9371136499
UK : +44-2081332571
Canada & USA : +1-4155992537
Some of the common countries from which patients travel to India for surgery are:
| USA | UK | Canada |
| Australia | New Zealand | Nigeria |
| Kenya | Ethiopia | Uganda |
| Tanzania | Zambia | Congo |
| Sri Lanka | Bangladesh | Pakistan |
| Afghanistan | Nepal | Uzbekistan |
Below are the downloadable links that will help you to plan your medical trip to India in a more organized and better way. Attached word and pdf files gives information that will help you to know India more and make your trip to India easy and memorable one.
 Fortis Hospital
Fortis Hospital Artemis Hospital
Artemis Hospital Max Hospital
Max Hospital Columbia Asia Hospital
Columbia Asia Hospital Medanta Hospital
Medanta Hospital


 Jaslok Hospital
Jaslok Hospital Lilavati Hospital
Lilavati Hospital


 Global Hospitals
Global Hospitals Jupiter Hospital
Jupiter Hospital